Teaching and Learning
Great Teaching and Learning Policy Rationale
Deptford Green School aspires to be a vibrant and dynamic learning environment in which every learner is given the opportunity to:
- Fulfil their academic potential and be able to achieve their ambitions for the next stage of their educational journey.
- Make a positive contribution to the school community and the wider community that we serve.
- Develop socially and emotionally the skills and attributes needed to live happy, safe and productive adult lives.
At Deptford Green we expect every lesson to be an engaging, compelling, challenging and enjoyable learning experience for both teacher and learner. To ensure a high quality and consistent approach, teachers will use the Deptford Green Teaching and Learning Wheel which incorporates the SSAT Learning Cycle to plan and deliver lessons including remote/independent learning. An expectation of exceptional progress for all learners will be embedded in every lesson. Independent Learning tools such as Class Charts will be used to enhance the progress of learners. This policy provides the framework for teachers to teach and learners to learn in an environment that is committed to excellence.
The Great Teaching and Learning Wheel (incorporating the SSAT Learning Cycle Lesson Framework)
The GREAT T&L wheel underpins GREAT T&L, GREAT Curriculum and GREAT CPD at Deptford Green School.
At the centre of our teaching is always ‘GREAT Learning’.
To do this, we use the six-phase lesson model based on the SSAT TEEP principles where we guide learners to ‘Prepare for Learning’ and ‘Agree Learning Outcomes’; ‘Present New Information’ and ‘Construct Meaning’ in creative ways; ‘Apply to Demonstrate’ and ‘Review’ learning in different lessons across schemes of work.
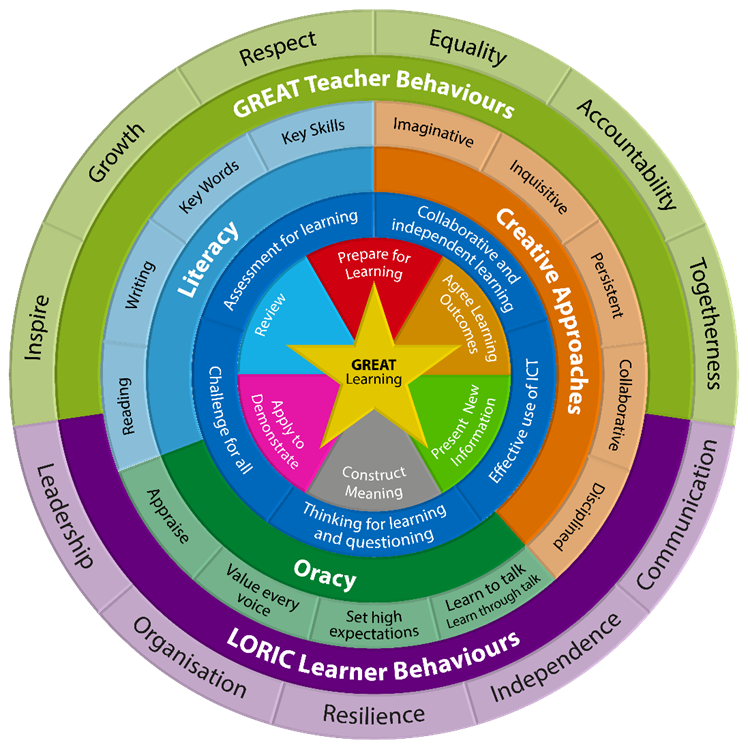
To ensure GREAT T&L, teachers use a range of ‘Assessment for Learning’ and ‘Collaborative and independent learning’ activities; they plan for ‘Effective use of ICT’, ‘Thinking for learning and questioning’ and differentiate to include ‘Challenge for all’.
Lessons and schemes of work are planned with a range of ‘Creative Approaches’ in mind to engage and inspire learners. These are underpinned by the delivery of Literacy and Oracy skills to ensure learners can communicate their ideas effectively.
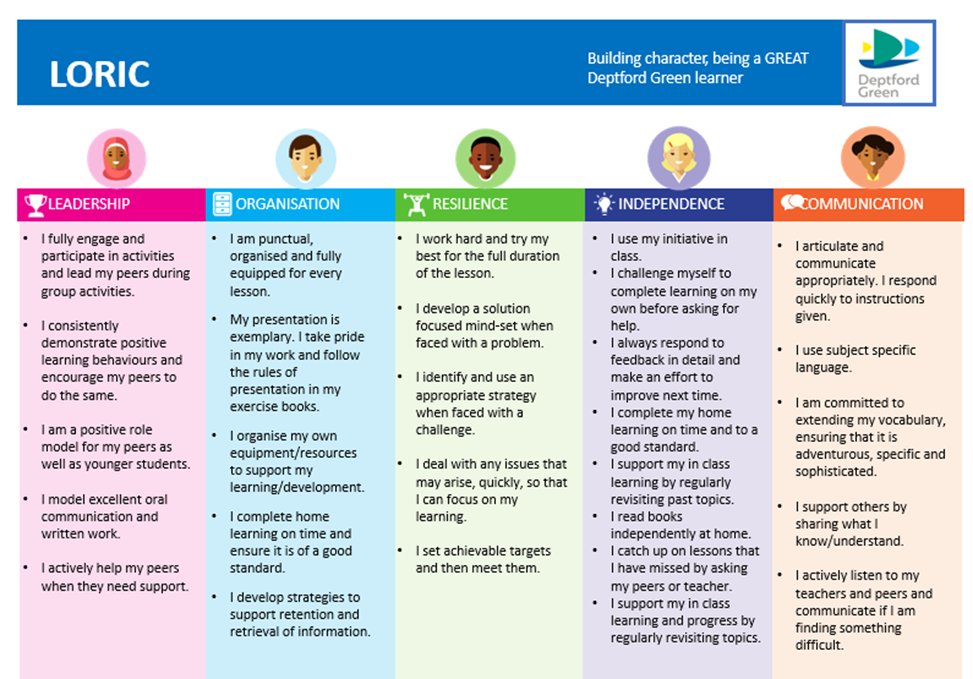
Wrapping around the GREAT T&L at Deptford Green School are the core values of ‘Growth’, ‘Respect’, ‘Equality’, ‘Accountability’, ‘Togetherness’ and to ‘Inspire’; and interpersonal skills: ‘Leadership’, ‘Organisation’, ‘Resilience’, ‘Independence’ and ‘Communication’ to ready students for the world of work and beyond.
Great Pedagogy
The way in which we deliver our lessons can have a significant impact on how much a student learns and remembers. Below are pillars we use to ensure consistent, high-quality pedagogy across all subjects. These pillars are used as the basis for temperature checks, Enquiry Walks and internal subject monitoring. Below each pillar is a success criteria.
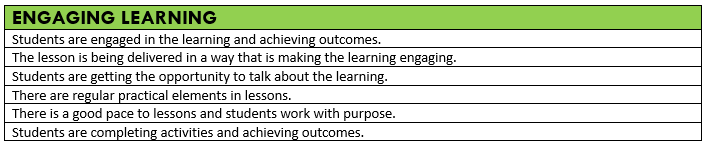
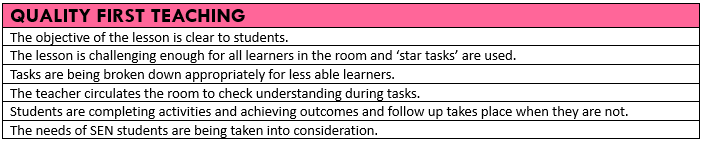
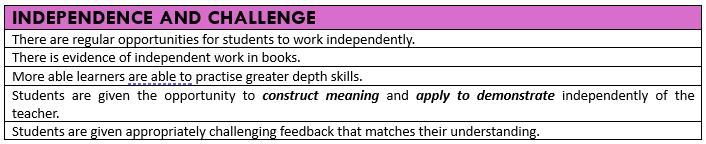
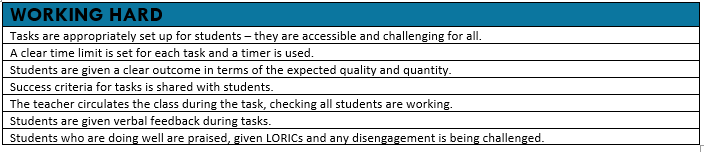

High Expectations, Praise & Reward
A key feature of our classrooms must be the praise and reward for the students who are getting it right. Below are the LORIC learner behaviours that we use to reward out students.
Great Effort
Our expectations of students must be consistently high. We use the following descriptors to ensure our students always get the most out of lessons. These descriptors are used for data drops and when students are being monitored on effort report.




